Pioneering Clean Energy: The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub’s Journey
At the vanguard of the United States’ clean energy frontier, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub (PNWH2 Hub) stands as a testament to the power of collective ambition and innovation. Orchestrated by the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Association, a multi-state coalition, the PNWH2 Hub exemplifies a regional endeavor, marrying the expertise of public and private partners from diverse sectors including Tribal Nations, industry, and academia across Washington, Oregon, and Montana.
With the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) selecting the PNWH2 Hub for award negotiations, the initiative is set to become a cornerstone in the nation’s burgeoning hydrogen economy. The hub is poised to receive up to $1 billion in federal funding over eight years, a move by the DOE that represents one of the agency’s most significant investments to date and a pivotal step in laying the groundwork for a national clean hydrogen network.

The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 Hub’s blueprint is one of ingenuity and foresight, targeting the hard-to-decarbonize sectors that are crucial to the region’s economic fabric, such as heavy-duty transportation, port operations, agriculture, and industrial processes. Leveraging the region’s abundant clean power and pioneering technology companies, the hub is set to catalyze the transition to renewable hydrogen production, with the goal of not just meeting, but surpassing DOE’s clean hydrogen production benchmarks.
This initiative is not just about clean energy; it is also about good-paying jobs and community prosperity, forecasting the creation or support of more than 10,000 jobs that will contribute to a robust and sustainable regional economy. With a solid community benefits plan spearheaded by Washington State University, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 is dedicated to ensuring that the clean hydrogen economy is inclusive and beneficial for all, linking hydrogen producers with consumers and guiding the region towards a greener future.
In this transformative phase of energy evolution, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 stands ready to propel the Pacific Northwest into a new era, where clean hydrogen is not a distant dream but an imminent reality, powering the economy and safeguarding the environment for generations to come.
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub Vision and Goals:
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub, known as the PNWH2, is conceived with a transformative vision that seeks to pivot the region—and ultimately the nation—towards a future where clean, renewable hydrogen fuels industries and powers transportation. This ambitious venture aims to construct a robust network of hydrogen production and consumption that focuses on sectors where decarbonization poses the most significant challenges, such as heavy-duty transportation, port operations, and industrial processes that are currently dependent on fossil fuels.
The goals of the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 are multifaceted. Primarily, the hub intends to exceed the Department of Energy’s production targets, aspiring to produce more than the 50 to 100 metric tons per day of clean hydrogen required. This goal is not just an environmental benchmark but also a statement of intent to lead the clean hydrogen industry in scale and efficiency.

Moreover, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 is committed to fostering economic growth and social equity. By leveraging the Pacific Northwest’s existing clean power and innovative technology firms, the hub is expected to support over 10,000 good-paying jobs, contributing significantly to the region’s economy and workforce development. These jobs are envisioned to span a range of skills and expertise, ensuring that the benefits of this green initiative permeate through various levels of the job market.
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 also places considerable emphasis on community benefits. Washington State University, a key player in the hub’s development, will lead the community benefits plan, ensuring that the growth of the green hydrogen economy is inclusive. Through its CHARGE consortium, the university aims to ensure that the hub’s developments are interconnected with both hydrogen producers and consumers, facilitating a seamless market lift-off for green hydrogen.
Economics and Community Impact
The economic and community impact of the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub is projected to be significant and far-reaching. As the hub moves forward with its objective to drive the region’s transition to a hydrogen economy, the anticipated creation of more than 10,000 jobs stands as a cornerstone of its economic promise. These positions, spanning from construction to long-term operational roles, not only denote a surge in employment opportunities but also signify the region’s commitment to bolstering a future-proof workforce within the clean energy sector.
This employment upsurge is expected to permeate various strata of the job market, offering positions that require diverse levels of skill and training. This inclusive job creation strategy is designed to ensure that the benefits of the hydrogen hub extend to all corners of the community, providing a stable economic foundation and a springboard for sustainable growth. See the similarities between this hub and The Midwest Hydrogen Hub.
Moreover, the The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen hub’s community impact is underlined by Washington State University’s leadership in orchestrating a comprehensive community benefits plan. This plan is intended to ensure that the burgeoning green hydrogen market is accessible and equitable. The university’s CHARGE (Collaboration for Hydrogen Advancement, Research, and Generation of Equity) consortium serves as a bridge, connecting hydrogen producers with end users, thereby facilitating a market environment where hydrogen can be produced, sold, and utilized efficiently and fairly.
Washington State University’s role in the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 goes beyond market facilitation. The institution is also set to play a pivotal role in research and development, harnessing its academic and technical expertise to address current and future challenges in hydrogen production and distribution, further solidifying the hub’s economic and communal propositions.
In essence, the PNWH2 Hub is expected to be more than an environmental endeavor; it is positioned as a catalyst for economic revitalization and community empowerment. By aligning the initiative with the region’s broader economic aspirations, the hub aspires to enhance the Pacific Northwest’s energy security and independence, while laying a foundation for long-term economic stability and social prosperity.
Infrastructure and Technology
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub is a beacon of progress in the realm of clean energy infrastructure and technology. At its core, the hub aims to leverage the Pacific Northwest’s existing strengths in renewable energy to establish a state-of-the-art hydrogen production and distribution network. The region’s abundant hydro-power and growing wind and solar sectors provide a robust clean energy backbone that will underpin the hub’s hydrogen production, setting a benchmark for environmental sustainability and technological innovation.
Key to the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub’s PNWH2 infrastructure strategy is the deployment of advanced electrolyzers, which are instrumental in the production of green hydrogen. These electrolyzers will harness the region’s clean electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, thereby eliminating carbon emissions from the production process. The technology companies in the Pacific Northwest, renowned for their innovative capabilities, are expected to play a significant role in refining these processes, enhancing efficiency, and scaling up production to meet the ambitious targets set by the hub.

Moreover, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen hub’s technological blueprint includes the development of a comprehensive distribution system that facilitates the storage and transportation of hydrogen to various points of use. This system will not only cater to local demand but is also envisioned to contribute to a broader national clean hydrogen network. The infrastructure plan encompasses both existing pipelines and new delivery modalities, all designed to ensure that hydrogen can be supplied reliably and cost-effectively to end-users across multiple sectors.
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub’s PNWH2 infrastructure and technology pathway is thus characterized by a forward-thinking approach that blends environmental goals with economic pragmatism. By capitalizing on the Pacific Northwest’s renewable energy resources and cutting-edge technological prowess, the hub is poised to create a scalable model for clean hydrogen development that can be adopted across the United States and beyond.
Partnerships and Key Players
The formation and ongoing development of the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub (PNWH2 Hub) are underpinned by a synergy of partnerships and the active participation of key players from various sectors. This collaborative framework is essential for realizing the hub’s ambitious goals.
At the forefront of these partnerships is the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub Association (PNWH2A), which acts as a pivotal connector among private entities, government bodies, academic institutions, and research organizations. The PNWH2A’s role is critical in aligning the diverse objectives and capabilities of each partner towards the common goal of establishing a thriving hydrogen economy in the region.
Washington State University (WSU) emerges as a vital academic and research participant, bringing its substantial expertise to bear on the hub’s development. WSU’s leadership in the community benefits plan via its CHARGE consortium highlights the university’s commitment to ensuring that the hub’s growth translates into tangible benefits for all community members. Additionally, WSU is tasked with connecting hydrogen producers and consumers to foster an efficient and equitable market.
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub PNWH2 also draws on the strengths of industry partners, including technology companies renowned for innovation in clean energy. These companies are expected to contribute significantly to the hub’s technological advancement, particularly in the areas of electrolyzer development and the improvement of hydrogen storage and transportation infrastructure. This industrial involvement is crucial, as these companies will be responsible for scaling up hydrogen production and bringing it to market in a commercially viable manner.
Together, these partnerships form the backbone of the The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub’s (PNWH2) strategy. The collaboration between academic research, industry expertise, and public sector support creates a comprehensive ecosystem designed to navigate the complex landscape of clean hydrogen production and utilization. This multifaceted alliance is not merely instrumental in achieving the hub’s short-term objectives but is also pivotal for laying the groundwork for long-term sustainability and success in the clean hydrogen arena.
Progress and Future Plans For The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub (PNWH2 Hub) is charting a progressive course, with notable strides already made and ambitious plans laid out for its future. The hub has successfully advanced to the final stages of the selection process for a federal funding award under the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) regional clean hydrogen hubs program. This eligibility for up to $1 billion over eight years is a testament to the confidence in the hub’s potential to significantly contribute to the nation’s clean hydrogen network.
In terms of progress, the hub has delineated a clear pathway to achieve its objectives. The initial phase involves meticulous planning and the establishment of a governance structure that ensures effective oversight and the seamless integration of the various stakeholders’ efforts. The inclusion of numerous partners from the government, industry, and academic sectors has already set a solid foundation for comprehensive collaboration.
Looking ahead, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub’s PNWH2 future plans are ambitious and well-defined. The hub aims to utilize the Pacific Northwest’s plentiful renewable energy resources to fuel clean hydrogen production, with a particular focus on advanced electrolyzer technologies. These efforts will be pivotal in reducing production costs and enhancing the efficiency of hydrogen as a reliable energy source. Furthermore, the hub intends to develop a robust infrastructure for hydrogen distribution, prioritizing safety, scalability, and environmental sustainability.
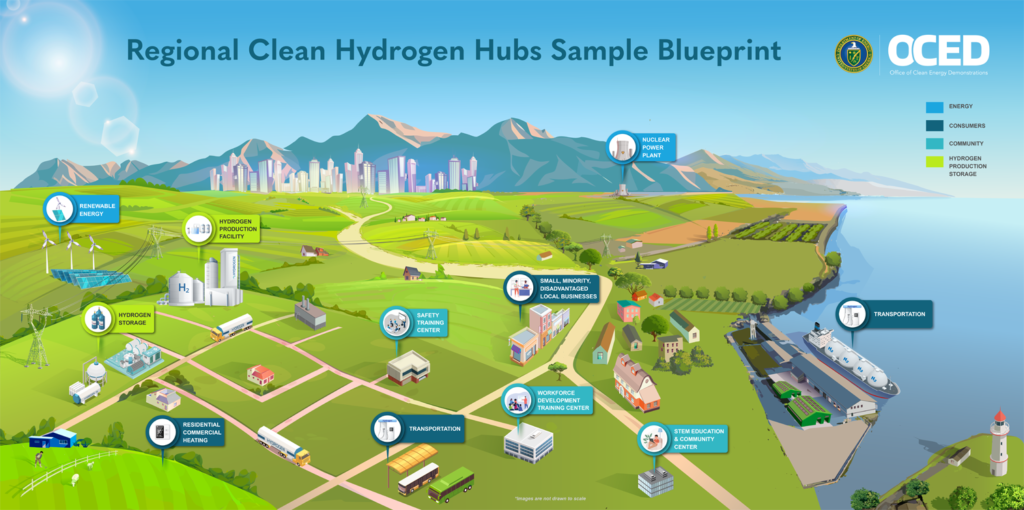
Community engagement and labor relations form another critical aspect of the hub’s future plans. The PNWH2 Hub is poised to engage in extensive dialogue with local communities and workforce’s, ensuring that the transition to a hydrogen economy is inclusive and equitable. Through initiatives such as the development of a community benefits plan led by Washington State University, the hub is dedicated to fostering a clean energy economy that offers ample opportunities for all residents and respects the unique needs and values of the local communities.
In essence, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub’s PNWH2’s future is one of innovation, community partnership, and economic transformation. With the dual goals of environmental stewardship and economic vitality guiding its trajectory, the hub is on course to become a leading example of how regional collaboration and strategic planning can create a sustainable and prosperous clean energy future.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub (PNWH2 Hub) confronts a landscape rife with challenges and opportunities, reflective of the broader transition to a clean energy economy. One of the primary challenges lies in de-carbonizing sectors that are traditionally reliant on fossil fuels, such as heavy industry and long-haul transportation. These sectors present significant technical and economic hurdles due to their energy-intensive nature and the current infrastructure that supports them. The PNWH2 Hub, through its focus on innovative hydrogen production and utilization technologies, is poised to address these challenges head-on. The hub’s approach involves not only developing new methods of clean hydrogen production but also retrofitting and adapting existing energy systems to accommodate hydrogen as a fuel source.
The opportunities that arise from these challenges are manifold. By advancing the technology and infrastructure for hydrogen energy, the PNWH2 Hub has the potential to position the Pacific Northwest as a leader in the clean energy sector, attracting investment and talent. This, in turn, could drive innovation in related industries, from advanced manufacturing to environmental technology, creating a ripple effect of economic growth and job creation.
Moreover, the PNWH2 Hub stands to play a crucial role in the broader national goal of establishing a clean hydrogen network, which could serve as a backbone for a more resilient and sustainable energy grid. The federal funding aimed at fostering regional hydrogen hubs reflects this strategic opportunity, providing the financial support necessary to overcome initial barriers to development and scale.
The PNWH2 Hub’s future plans include robust research and development initiatives, community engagement efforts, and the formulation of strategies to navigate the regulatory and market challenges associated with introducing a new energy paradigm. The hub’s commitment to community and labor relations ensures that the transition to a hydrogen economy is not only technologically sound but also socially inclusive and just. The Heartland Hydrogen Hub offers similar opportunities for the community to thrive.
The PNWH2 Hub is navigating a path through a complex array of challenges and opportunities with a strategic focus on innovation, economic growth, and community partnership. Its success will likely hinge on its ability to remain adaptable and responsive to the evolving energy landscape, ensuring that the clean hydrogen economy it aims to build is both environmentally sustainable and economically robust.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub (PNWH2 Hub) emerges as a paradigmatic initiative, charting a course towards a sustainable and resilient clean energy future. As a front-runner in the U.S. Department of Energy’s regional clean hydrogen hubs initiative, the PNWH2 Hub is poised to leverage up to $1 billion in federal funding to catalyze its vision. This substantial investment underscores the hub’s potential to significantly impact the nation’s clean energy trajectory.
The PNWH2 Hub’s comprehensive approach integrates cutting-edge technology, expansive infrastructure development, and collaborative partnerships across public and private sectors, academic institutions, and community organizations. It is this multifaceted collaboration that forms the nucleus of the hub’s strategy, driving forward its mission to realize a robust hydrogen economy in the Pacific Northwest.
The hub’s future plans are not without challenges, yet it is these very challenges that present unparalleled opportunities for innovation and growth. By pioneering efforts to de-carbonize hard-to-electrify sectors, the PNWH2 Hub is not just advancing environmental goals but also fostering economic development and job creation, ensuring that the benefits of a clean hydrogen economy are shared widely and equitably across communities.
As the PNWH2 Hub advances, it remains a beacon of the collaborative spirit and strategic importance required for success in the broader context of clean energy development. It stands as a testament to the transformative power of shared vision and collective effort, promising to shape not only the energy landscape of the Pacific Northwest but also to contribute significantly to the national and global clean energy dialogue.


